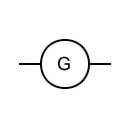
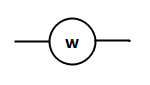
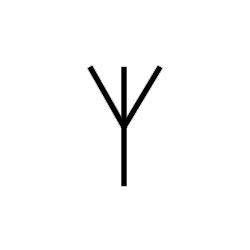
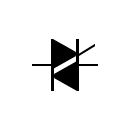A light bulb is an electrically powered device that produces light by passing an electric current through a filament or a gas-filled tube. The electric current heats the filament or excites the gas, causing it to emit photons, which generate visible light. Light bulbs come in various types, including incandescent bulbs, fluorescent tubes, compact fluorescent lamps (CFLs), and light-emitting diode (LED) bulbs, each with its own characteristics and efficiency. Light bulbs are used for general lighting purposes in homes, offices, and public spaces, providing illumination for tasks, safety, and ambiance. They have undergone significant advancements over the years, with newer technologies like LEDs offering greater energy efficiency and longer lifespans compared to traditional incandescent bulbs.